Developing novel Wireless Sensor modalities to aid Robot Automation.
A recent spur of interest in indoor robotics has increased the importance of robust simultaneous localization and mapping algorithms in indoor scenarios. This robustness is typically provided by the use of multiple sensors which can correct each others’ deficiencies. In this vein, exteroceptive sensors, like cameras and LiDAR’s, employed for fusion are capable of correcting the drifts accumulated by wheel odometry or inertial measurement units (IMU’s). However, these exteroceptive sensors are deficient in highly structured environments and dynamic lighting conditions. This letter will present WiFi as a robust and straightforward sensing modality capable of circumventing these issues.
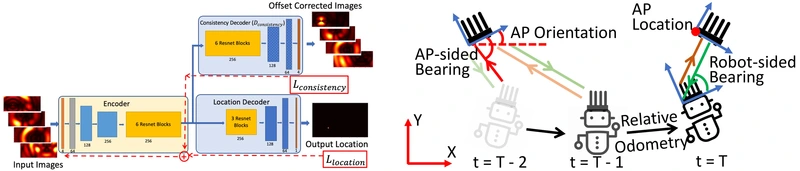
The idea is to be able to readily integrate Wi-Fi as an alternative to GPS for indoor navigation for robotics as shown above. We have already demonstrated the use of WiFI for robotic navigation as shown above, where the robots movement over three timestamp are shown in the fiture at the center, and have also designed a toolbox that can readily integrate Wi-Fi for robotics into the existing SLAM algorithms.
Aditya Arun, Roshan Ayyalasomayajula, William Hunter, and Dinesh Bharadia
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022
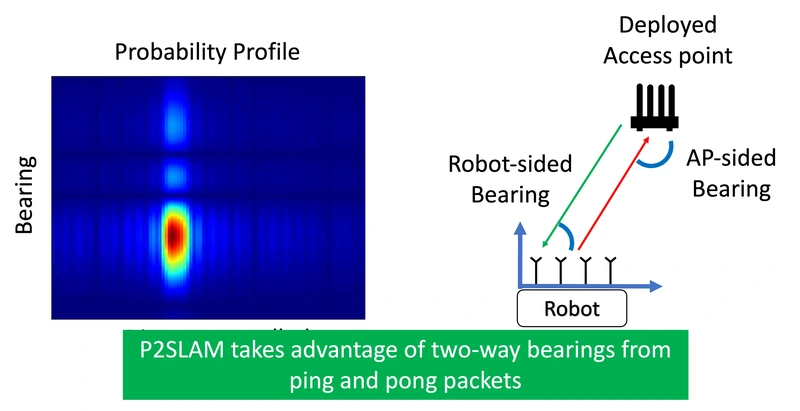
Aditya Arun, William Hunter, Roshan Ayyalasomayajula, and Dinesh Bharadia
arXiv preprint arXiv:2209.08091, 2022
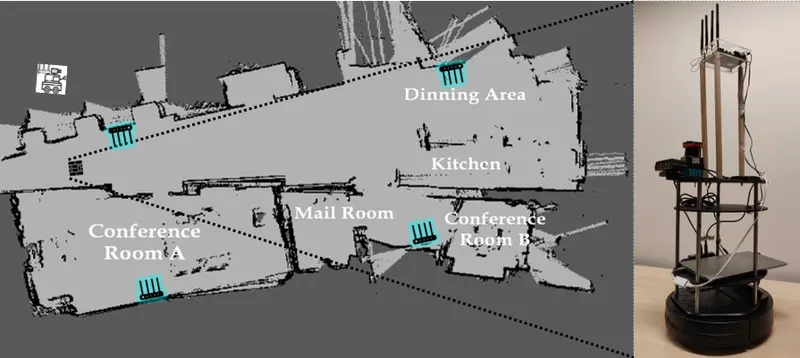
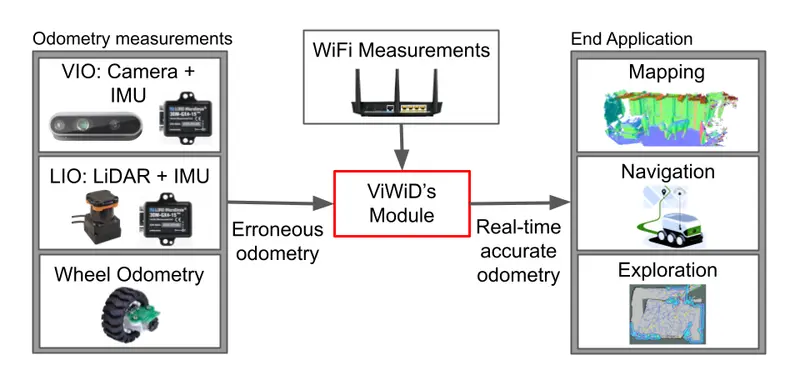
Roshan Ayyalasomayajula, Aditya Arun, Chenfeng Wu, Shrivatsan Rajagopalan, Shreya Ganesaraman, Aravind Seetharaman, Ish Kumar Jain, and Dinesh Bharadia
In 17th USENIX Symposium on Networked Systems Design and Implementation (NSDI 20), 2020